CT Stories
Telecom equipment-A challenging 2024 ahead

The worldwide telecom equipment market in 2023 is estimated to have advanced by 2 percent in H1 2023, according to Dell’Oro. However, performance by region and technology varied. After five years of expansion, during which the North America region advanced by around 50 percent, the pendulum swung toward the negative in the first half. The decline in North America was anticipated, but the pace of the contraction was slightly faster than expected. Alongside more challenging 5G comparisons and inventory corrections affecting some technology segments, North American broadband-access equipment spending dropped to its lowest levels in nearly two years in the second quarter.
Stable performance in EMEA, CALA, and China, combined with robust growth in the Asia-Pacific region outside of China, offset the weakness in the US market. Worldwide telecom equipment revenues, excluding North America, increased by 7 percent in the first half, supporting the thesis that the telecom equipment market remains robust outside of the US.
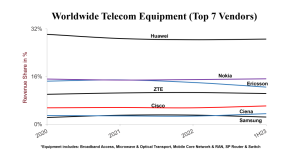
Source: Dell’Oro
Vendor dynamics remained mostly stable between 2022 and H1 23, with a few exceptions. Ciena surpassed Samsung, as the vendor is growing as supply chain and product investor pressures ease, as was reflected in its latest financial results. The gap between Nokia and Ericsson widened, reflecting, to some extent, the technology mix between wireless and wireline. Nokia’s market share held firm, thanks to its broad portfolio of wireline as well as mobile network infrastructure products, whereas Ericsson’s share dipped due to its greater reliance on wireless network spending.
Despite ongoing efforts by the US government to limit Huawei’s addressable market and access to the latest silicon, analysis shows that Huawei still leads the global telecom equipment market. This is partly because Huawei remains the #1 supplier in five out of the six telecom segments tracked, and the vendor continues to dominate the market outside of North America, accounting for 35 percent to 40 percent of H1 2023 revenues.
From a technology perspective, RAN declined, but the remaining five programs advanced in the first half. Notably, wireline outperformed wireless. Analysis indicates that the collective results for the wireline-focused programs (SP routers and switches, optical transport, and broadband access) increased by around 7 percent in the first six months. This, coupled with the positive trends in mobile core networks and microwave transmission, was more than enough to offset the more challenging conditions in RAN.
RAN. The economic forces that have shaped the radio access network (RAN) market over the past 30-plus years are expected to influence risk appetite and RAN investments for the remainder of this decade. Despite the current period of heightened uncertainty and increased skepticism about the telecom and RAN outlook, long-term perspective on this market remains unchanged. The tangible and intangible assets operators have amassed over the past decades are essential for addressing the evolving connectivity needs of consumers and businesses. While new business models and competitors will emerge, operators will continue to play a leading role in providing connectivity by the end of this decade.
At the same time, RAN’s growth prospects remain challenging. Operators can increase capital intensities over the short term to support the deployment of new technologies, but this acceleration tends to be temporary, resulting in a relatively flat RAN trendline over time, ultimately limited by operator revenue trends. The potential upside from emerging opportunities, including fixed wireless access (FWA) and private wireless, will play a crucial role in compensating for tepid mobile broadband (MBB) advancements.
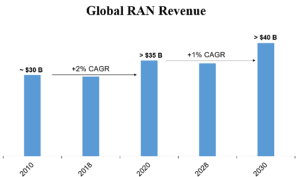
Source: Dell’Oro
After growing at a 2-percent CAGR in the 4G era, global RAN revenues are projected to increase at a 1-percent CAGR between 2020 and 2030. The base case scenario is built on the assumption that RAN revenues peaked in 2021, and will continue to trend downward before picking up momentum in the outer part of the forecast period.
Other forecast include:
- Cumulative 2020–2030 RAN revenues are projected to surpass USD 0.4 trillion.
- Macro RAN deployments will dominate the first 6G wave.
- Cloud RAN is expected to play a leading role from the start with 6G.
- Small cells will comprise ~15 percent of the 2030 RAN market.
Optical Transport equipment revenue grew 5 percent year-over-year (YoY) in Q2 2023. This was the third consecutive quarter that the optical market growth rate topped estimates. The better-than-expected revenue was due to higher DWDM long-haul and multiservice multiplexer revenue.
The largest global WDM suppliers in the trailing four quarter period were Huawei, Ciena, Nokia, ZTE, Infinera, and FiberHome. Among these vendors, Nokia and FiberHome gained the most market share compared to the previous year period. FiberHome’s optical revenue grew at the highest rate among the vendors at over 30 percent YoY.
“It was another great quarter for optical system vendors,” said Jimmy Yu, vice president at Dell’Oro Group. “Ever since component supply eased up, system manufacturers have been able to deliver more products to their customers that sat in backlog. As a result, optical revenues have increased at a faster rate than expected. With that said, some customers are signaling a need for a little pause after receiving these deliveries. Therefore, even though the results in the first half of 2023 were higher than expected, we are holding the full-year 2023 outlook at 4 percent, believing YoY growth will slow in the back half of the year,” added Yu.
Sales of PON equipment for fiber-to-the-home deployments, cable broadband access equipment, and fixed wireless CPE will show a 0.2-percent compounded annual growth rate (CAGR) from 2022 to 2027, as service providers continue to expand their fiber and DOCSIS 3.1/4.0 networks, while also increasing the reliability and sustainability of their broadband access networks.
PON equipment revenue is expected to grow from USD 11.8 billion in 2022 to USD 13.3 billion in 2027, driven largely by XGS-PON deployments in North America, EMEA, and CALA.
Revenue for cable distributed access equipment (virtual CCAP, remote PHY devices, remote MACPHY devices, and remote OLTs) is expected to reach USD 1.6 billion by 2027, as operators ramp their DOCSIS 4.0 and fiber deployments.
Revenue for fixed wireless CPE is expected to reach USD 2.7 billion by 2027, led by shipments of 5G sub-6GHz and 5G millimeter wave units.
Revenue for residential Wi-Fi routers will surpass USD 5.2 billion in 2027, owing to massive shipments of Wi-Fi 7 units.
“After three consecutive years of tremendous broadband network expansions and upgrades, 2023 is expected to show a return to normalized levels of spending,” said Jeff Heynen, vice president of Broadband Access and Home Networking research at Dell’Oro Group. “After 2023, spending is expected to increase through 2026 and 2027, driven by 25 Gbps and 50 Gbps PON, fixed wireless CPE, as well as DAA and DOCSIS 4.0 deployments.”
The coherent optical transceiver shipments are expected to grow at a 17-percent compounded annual growth rate (CAGR) for the next five years. Additionally, the coherent optics market is undergoing a tectonic shift with the availability of small form factor pluggable optics that will increase the use of coherent technology in routers and Ethernet switches.
“The demand for coherent technology is expanding,” stated Jimmy Yu, vice president for Optical Transport Market Research at Dell’Oro Group. “This is in part due to the continuous need for better, lower powered, and higher-capacity transceivers that meet future global network requirements,” added Yu.
“Historically, the majority of coherent optics have predominantly found their application in DWDM systems,” stated Sameh Boujelbene, vice president for Ethernet Switch Market Research at Dell’Oro Group. “However, with vendors making strides in developing smaller and more energy-efficient coherent transceivers, the scope of their use is rapidly expanding. This expansion encompasses not only the range of platforms they can support, but also the diversity of applications to which they can cater,” added Boujelbene.
Additional highlights
- Coherent optics market is predicted to reach nearly USD 13 billion by 2027. This growth will be driven by both form factors – module/embedded and plug. Pluggable transceivers are projected to grow at the highest rate, and contribute most of the volume growth for the next five years.
- The use of coherent transceivers on DWDM systems will continue to contribute the largest share of the market revenue. However, within a short period of time, the use of coherent optics on router and switch platforms will reach material levels.
- Coherent optics deployed on router and switch platforms will account for more than 50 percent of the annual increase in transceiver shipments throughout the forecast period. This will be due to the availability of ZR Optics, beginning with 400ZR and carrying through to 1600ZR.
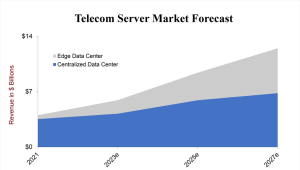
The telecom server market is projected to experience a robust 19-percent CAGR over the next five years, reaching USD 12.5 billion by 2027. Fueled by the increasing adoption of network function virtualization (NFV) and the growing momentum of edge use cases, it is slightly outpacing the overall data center growth rate of 15 percent. This adjustment comes as projections for the data center market, driven by increased investments in accelerated computing for artificial intelligence (AI) applications have been raised.
The convergence of data center IT and telecom infrastructure continues, with service providers (SPs) favoring commercial off-the-shelf (COTS) servers for network function virtualization (NFV) to reduce costs, replacing dedicated hardware. Recent supply chain disruptions have highlighted a preference for standardized, commoditized servers over specialized equipment, enabling broader applications through virtualization.
As telecom embraces open network architectures and the edge gains momentum, the competitive server market is poised for growth. The edge, projected to represent 45 percent of telecom server revenue by 2027, promises resilience, efficiency, and immersive experiences, prompting vendors to compete for dominance in this evolving landscape.
Relative to October 2022, the forecast for the telecom server market has been lowered. This is due to a few factors, including economic headwinds leading to reduced spending on mobile network infrastructure, and challenges with the adoption of open RAN and MEC.
The transition of telecom appliances to server-based architectures is still in its early stages, even when compared to the evolution of cloud computing.
Additional forecast include:
- Centralized data center use cases, encompassing MCN and other internal IT workloads, are expected to grow at an 11-percent CAGR in revenue from 2022 to 2027, while edge data center cases, covering MEC, RAN, and broadband access, are anticipated to grow by 38 percent during the same period.
- Server revenue for edge data centers is expected to achieve a significantly higher growth rate compared to that of centralized data centers for telecom applications. We anticipate changes in the ecosystem as telecom edge infrastructure adoption increases. Servers in centralized data centers for telecom applications will resemble those from traditional IT vendors like Dell, HPE, and Lenovo. In contrast, we anticipate a wider range of solutions from both server and telecom equipment vendors for edge data centers. These systems will be designed to handle harsh environmental conditions and security challenges in remote areas.
- The implementation of AI at both the network core and edge is expected. At the core, AI engines could be utilized to automate real-time and near-real-time decision making, based on raw data from internet traffic and allocate network resources in real-time dynamically. At the edge, new AI use cases, primarily related to computer vision, that could enable applications, such as industrial automation, autonomous driving, security, and various consumer services.
Source: Dell’Oro
The Mobile CoreNetwork (MCN) market has become erratic, with the lowest growth rate since Q4 2017. Europe, Middle East, and Africa (EMEA), and China were the weakest performing regions in Q3 2023.
Two new MNOs launched commercial 5G SA networks in Q3 2023 – Telefónica O2 in Germany and Etisalat in the UAE.
Ericsson is the vendor of record for the 5G packet core for all seven 5G SA networks launched in 2023. As of Q3 2023, 45 MNOs have commercially deployed 5G SA eMBB networks. The top MCN vendors worldwide for Q3 2023 were Huawei, Ericsson, Nokia, and ZTE. The top 5G MCN vendors worldwide for Q3 2023 were Huawei, Ericsson, ZTE, and Nokia.
“It has become quite obvious the MCN market has entered into a very unpredictable phase after breaking the highest growth rate in Q2 2023 since Q1 2021, and now hitting the lowest performing growth rate in Q3 2023 since Q4 2017. Last quarter, EMEA and China were the strongest performing regions and flipped this quarter, becoming the weakest performing regions,” stated Dave Bolan, research director at Dell’Oro Group. “Many vendors state that the market is volatile, attributing this phenomenon to macroeconomic conditions, such as the fear of higher inflation rates, unfavorable currency foreign exchange rates, and the geopolitical climate.
“Besides subscriber growth, the growth engine for the MCN market is the transition to 5G Standalone (5G SA), which employs the 5G Core. But after five years into the 5G era, we are still seeing more 5G non-standalone (5G NSA) networks being launched than 5G SA, and the pace of 5G SA networks has slowed from 17 launched in 2022 to only seven so far in 2023. However, we expect more 5G SA networks to be deployed in 2024 than in 2023, and we expect 2024’s market performance to be better than 2023,” continued Bolan.
The cumulative revenue for microwave transmission equipment in the next five years is forecast to be USD 18 billion, which is 12 percent higher than the revenue achieved in the last five years. The market grew 5 percent YoY in Q2 2023, driven by both mobile backhaul and the vertical markets. The overall market forecast for 2023 is unchanged at an expected growth rate of 5 percent.
The E/V band market segment reached a new record revenue amount in the quarter. For the trailing four quarter period, the revenue was approximately USD 600 million.
Huawei and Ericsson captured the majority of the E/V band market in the quarter with a combined market share of more than 70 percent. Other major E/V band vendors include Nokia, Siklu, and ZTE.
Demand for mobile backhaul equipment, consisting of both wireless and fiber systems, to be used in 5G networks, is forecast to grow at a five-year compounded annual growth rate (CAGR) of nearly 20 percent.
The microwave transmission market is projected to peak in 2025 as the rate of growth in 5G deployments begins to slow the following year. Annual shipments are expected to reach a height of 1.8 million at that time.
The forecast for packet microwave in the Asia-Pacific region has been increased due to greater demand in India.
“Demand for microwave transmission gear is on the upswing,” said Jimmy Yu, vice president of Dell’Oro Group. “The growing number of 5G rollouts occurring globally is feeding the need for more wireless mobile backhaul. This is especially true for E-band systems since they were designed to efficiently transmit multiple gigabits of bandwidth. Hence, we are projecting shipments of E-band radios to grow at a 22-percent CAGR for the next five years,” added Yu.
Shipments of E-band microwave transmission equipment grew 77 percent YoY in Q2 2023. The top two vendors, Huawei and Ericsson, held the vast majority of this market’s share.
“Demand for E-band microwave equipment really picked up in the past three quarters,” stated Jimmy Yu, vice president at Dell’Oro Group. “A lot of these systems are being installed in India as the operators in that country quickly ramp up on 5G. Network rollouts and upgrades to 5G are happening at a really fast pace there. On top of this, the use of E-band is steadily moving beyond shorter spans that are under a kilometer to longer spans that are over a couple kilometers. Longer reach is a benefit of the newer radios, designed with higher transmit power and active antenna for site-to-site alignment,” added Yu.
The analyst team has not made any significant changes to the collective short-term outlook. Following five consecutive years of growth, worldwide telecom equipment revenues are projected to remain flat in 2023. As always, there are risks in both directions. In addition to currency fluctuations, economic uncertainty, and elevated interest rates, inventory adjustments, new technology rollouts, and the anticipated impact of national subsidization efforts can impact steady-state assumptions for various regions.
The research firm intimated those conditions will remain challenging in 2024 before stabilizing in 2025. Worldwide telecom CapEx is projected to drop 7 percent by 2025, relative to 2022.
Its broader telecom outlook is mostly unchanged. Global telecom CapEx is projected to decline at a 2-percent CAGR over the next three years, as growth in India and stable trends in Europe will not be enough to offset steeper CapEx deceleration in North America.
The transition toward steady-state conditions in the US will primarily affect wireless activity, leading to a 25 to 30-percent reduction over the next three years. Further, given the doubtful prospect of a change in the current revenue trajectory and the expectation of flat operator top-line growth, capital intensity ratios are approaching 16 percent by 2025, slightly below the current trendline.
“The forces that shape the CapEx cycle have not changed,” said Stefan Pongratz, VP of Dell’Oro Group. “Operators can raise capital intensities over the short term, but there is a reason the trend line has stayed flat over the past 10+ years.”
He added, “Since we are now operating at elevated ratios, CapEx acceleration remains a transitory phenomenon in a world where neither 4G nor 5G has been able to change the revenue trajectory.”















You must be logged in to post a comment Login