Industry
Seven companies continue to hold sway over the global telecom equipment market

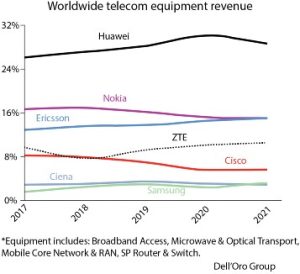
2021 marks the first year of market share erosion for the Chinese vendor, Huawei. Even so, Huawei continued to lead the global market, underscoring its grip on the Chinese market, depth of its telecom portfolio, and resiliency with existing footprints.
The overall telecom equipment global market advanced 7 percent in 2021, recording a fourth consecutive year of growth, underpinned by surging wireless revenues and healthy demand for wireline-related equipment, spurred on by double-digit growth both in RAN and Broadband Access. While there was a positive Q3 momentum, driven by strong growth in RAN and broadband access including surging demand for 5G and fixed wireless access CPEs, the fourth quarter 2021 displayed weaker momentum, and can be attributed to external factors, including Covid-19 restrictions and supply chain disruptions.
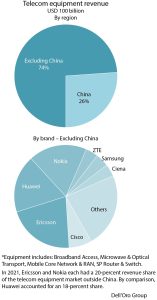
The collective global share of the leading suppliers remained relatively stable between 2020 and 2021, with the top seven vendors comprising around 80 percent of the total market. ZTE and Samsung are the two companies that are on an upswing year-to-date. Nokia and Ericsson each had around 15 percent share of total revenues, compared to about 29 percent for Huawei alone. Another 20 percent or so was taken by ZTE (11 percent), Cisco (6 percent), Samsung (3 percent), and Ciena (3 percent).
Total worldwide telecom equipment revenues approached USD 100 billion, up more than 20 percent since 2017. This includes equipment segments of broadband access, microwave and optical, transport, mobile core network and RAN, and SP router and switch.
Dell’Oro Group expects the annual growth to decline to 2 percent in 2022.
2021 marks the first year of market share erosion for Huawei. Huawei continued its struggle to stay afloat and remain relevant in the global market in the face of US trade sanctions and Washington’s pressure on its economic allies to bar use of the Chinese firm’s 5G equipment because of security concerns. The vendor has repeatedly denied US accusations of security issues. Even so, Huawei continued to lead the global market, underscoring its grip on the Chinese market, depth of its telecom portfolio, and resiliency with existing footprints. Its total market share slid almost 2 percent through Q3 2021 on an annualized basis, bringing it back to its 2019 levels with slightly more than 28 percent of the total market.
In the first three quarters, Huawei generated revenue of CNY 455.8 billion (USD 71.5 billion) with net profit margin of 10.2 percent. That compares to network equipment rivals Ericsson and Nokia, which in the first nine months of 2021, reported respective net sales of SEK 161 billion (USD 17.78 billion) and EUR 15.788 billion (USD 17.85 billion).
Huawei expects a 28.9-percent decline in total revenue for 2021 from 891.4 billion yuan to 634 billion yuan (USD 99.48 billion), following two years of US trade restrictions that have wreaked havoc on its once-lucrative smartphone business. “An unpredictable business environment, the politicization of technology, and a growing de-globalization movement all present serious challenges,” said rotating chairman Guo Ping in a New Year letter to his employees. “We need to stick to our strategy and respond rationally to external forces that are beyond our control. 2022 will come with its fair share of challenges, but we will keep working closely with our global partners to overcome the difficulties we face, improve business performance, and strengthen our foundations. We will continue investing in the future and creating value for our customers and partners. In the end, we will not only survive, but do so sustainably,” Guo added.
The company said that last year it saw solid growth in its enterprise business and stability at its carrier business. Its portfolio of telecom equipment includes broadband access, microwave, and optical transport systems, as well as mobile core network and RAN.
Since late 2020, Huawei has pursued initiatives to diversify its operations. These include drawing up plans to co-develop a luxury electric sport-utility vehicle, selling refurbished smartphones and licensing its handset designs, expanding its cloud services operations in the Asia-Pacific region, helping domestic enterprises cut their carbon footprint, supplying more 5G base stations and core network gear to China’s major telecom operators, establishing partnerships for its HarmonyOS mobile platform and divesting its Honor budget smartphone business.
Huawei’s lead in the equipment market contrasts its consumer smartphone business, which was hurt by the US sanctions and earlier placement on the Commerce Department’s Entity List in 2019.
Huawei held 17-percent share of global smartphone shipments in the first quarter of 2020 but contracted rapidly after Q2 2020, declining to just a 4-percent share in Q1 2021, according to Counterpoint Research. It spun off its budget smartphone brand Honor so it could survive and gain access to key components that were cut off as part of US actions – after which Honor in August became the third-largest smartphone brand in China in the low-mid-segment with 15-percent share. Apple in October moved to the No. 1 position in China with 22-percent share of smartphone sales in the country, ahead of Vivo and Oppo, as well as Huawei, who trailed the premium smartphone market with just 8 percent share. Huawei’s Q3 results showed trouble in consumer business as overall sales plunged 38 percent. Huawei did not break out its quarterly results by business segment, but attributed revenue declines to consumer.
Despite this year’s slide, Huawei’s control of the telecom equipment market now dates back to 2014, when Nokia barely edged it out for the top spot in Dell’Oro Group’s annual rankings. Nokia’s market share has declined every year since then, and Huawei posted annual year-over-year gains until 2021.
2021 was a strong year for Nokia, driven by its growing technology leadership, robust demand, and a faster-than-expected reset of its business. This enabled the vendor to deliver 3 percent constant currency net sales growth and a comparable operating margin of 12.5 percent. All the business groups made significant progress this year to make it more competitive in all the markets in which it competes.
Nokia entered 2022 in a strong position with improved margins, faster-than-expected strategy execution, and a high order backlog, although the global supply chain situation remains tight. Opportunities abound in the 5G rollout and growing enterprise market. Accordingly, 2022 is expected to bring another year of sales growth and the vendor is targeting a comparable operating margin of 11–13.5 percent in 2022, and the long-term target is to grow faster than the market and to achieve a comparable operating margin of at least 14 percent.
Nokia maintains an increasingly narrow lead over Ericsson, but just barely. Ericsson’s market share grew less than 1 percent year-over-year during Q3, and both Nokia and Ericsson ended the period with slightly less than 15-percent market share each.
Ericsson Group’s organic sales grew by 4 percent, with an increase in Networks sales of 7 percent. Reported sales were stable at SEK 232.3 billion. The loss of market share in Mainland China impacted sales by SEK –7.7 billion, and the growth rate by –3 percentage points, meaning that excluding Mainland China, organic sales growth was 8 percent.
ZTE, posted its third consecutive year of market share gains, landing almost 11 percent of the market through Q3 this year. ZTE’s annual results reported an operating revenue of 114.52 billion yuan (USD 18.12 billion), an increase of 12.9 percent compared with 2021. The comprising operating revenue from the domestic and the international markets reached 78.07 billion yuan (USD 12.35 billion) and 36.45 billion yuan (USD 5.77 billion) respectively, a year-on-year growth of 59.9 percent, with basic earnings per share of 1.47 yuan. The company attributed its growth in the domestic market to its deep involvement in large-scale 5G construction in China and the opportunities it seized for development in new infrastructure to empower digital transformation in various industries.
Meanwhile, Cisco reversed three consecutive years of market-share erosion, ending the first nine months of 2021 with almost 6 percent of the market. Samsung surpassed Ciena for the No. 6 spot this year, pushing its total share of the market above 3 percent. Finally, Ciena’s market share remained flat at 3 percent.
Risks are broadly balanced. In addition to the direct and indirect impact of the war in Ukraine and the broader implications across Europe and the world, the industry is still contending with Covid-19 restrictions and supply chain disruptions. At the same time, wireless CapEx is expected to surge in the US this year.















You must be logged in to post a comment Login