5G
5G driving the next growth wave for Digital India

5G is set to become a connectivity fabric for the country, says KPMG India in its recently released report at India Mobile Congress 2022.
Being the second largest mobile internet base, India has already cemented its place in the global telecom space. Now that the much awaited 5G spectrum auctions have been completed on the back of structural and policy changes, India is poised for a digital revolution. The next-gen digital services are expected to transform the way consumers connect, enterprises digitalise businesses, citizens consume government services, and the way Communications Service Providers (CSPs) bridge future communication needs with the current network transformation.
5G is set to become a connectivity fabric that connects people, devices, machines and ecosystems in a time of hyperconnectivity and quick technological advancements. With the low penetration of fixed broadband, 5G is set to deliver on the nation’s dream to remove the digital divide and provide connectivity to citizens of Bharat. 5G trials have demonstrated the power of 5G FWA to bridge the digital divide by enabling access to high-speed broadband in rural areas. The recent trials also demonstrated the power of connected India, where there is a free flow of essential services like education, healthcare, e-governance through digital mediums. Use-cases from smart farming to remote healthcare to use of AR/VR for skilling could go a long way in digitally enabling the success of Bharat.
Similarly, low latency, improved bandwidth and large machine-type communications, which are typical characteristics of 5G, are expected to have a significant positive impact on businesses. As per KPMG’s enterprise digital transformation survey, most businesses are already considering how 5G will benefit their process of digital transformation because of its service-based, cloud-native design and enhanced capabilities to support adoption of technologies like AI, IoT, robotics etc.
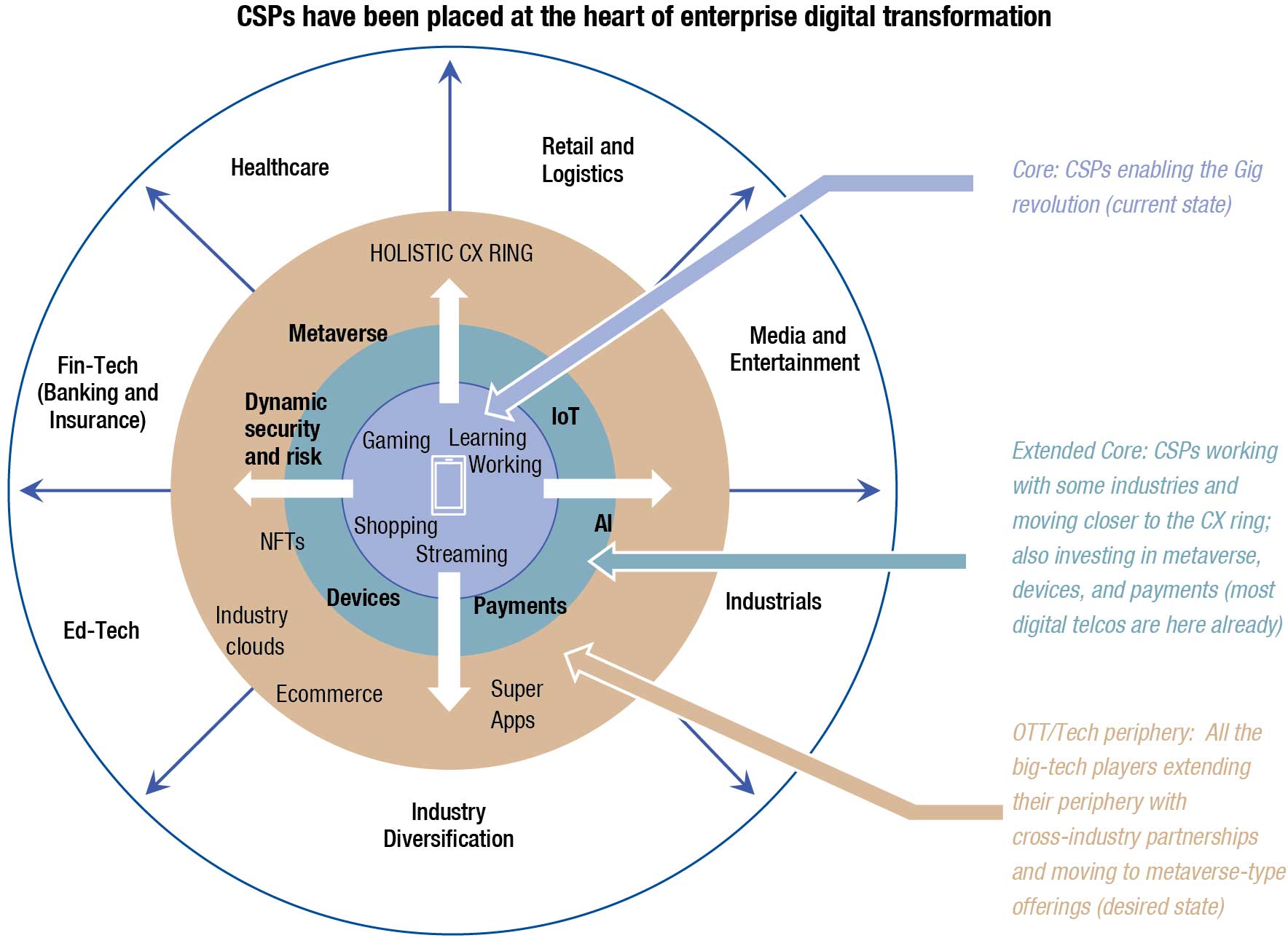
Growth, competition and the switch to 5G technology in existing 4G networks have greatly raised demand on CSPs to improve efficiency. From an operational and technological standpoint, the change to a more decomposed and open architecture for existing CSP environments is essential. To be ready for this opportunity, CSPs first will have to be agile in bringing this internal transformation up to speed and that will allow them to cater to newer revenue streams. As our survey indicated that as on date, CSPs are not the go-to vendor category for building enterprise capabilities in IoT, AR/VR, cloud or even AI/ML. To increase their pie of revenues, CSPs will have to look at creating capabilities beyond connectivity and create holistic solutions that deliver business value to enterprises. With 5G, CSPs will need to adapt to the new requirements which demand flexibility, openness, resiliency, reliability – all at a lesser cost and continual technology innovation.
Given the distinctiveness of India’s telecom industry and infrastructure status, it is crucial that mobile broadband remains at the centre of the country’s policy vision as India moves toward 5G and aims to fulfil its digital goals and ambitions. To genuinely make 5G an inclusive technology, emphasis should be put on how it affects the lives of rural and economically underserved communities.
Eliminating the digital divide remains a crucial aspect for government which not only aims to reach the last mile but also enable empowerment of MSMEs and SMEs through digitalisation. For this to happen, skill enhancements for the sector coupled with sufficient R&D budget allocation remains crucial for holistic national growth.
Furthermore, fiberisation of towers, virtualisation/softwarisation of telecom assets and capital outlay on small cells and street furniture is essential for realising 5G’s true potential.
The Draft Telecommunication Bill 2022 is a step in the right direction, as it consolidates the legal framework replacing existing laws with future ready legislation and aims at reducing ambiguity and promoting ease of doing business. The industry bodies, enterprises as well as government should consider brainstorming and building consensus on operationalizing this framework.
The KPMG report, provides a roadmap to organisations in ICT sector to re-purpose, re-engineer and re-position their offerings for an increasingly complex and demanding enterprise world. It also offers recommendations for a successful 5G roadmap and implementation.
Key highlights
- Approximately 50 per cent of Indian enterprises point towards increased budgets, especially for non-time critical communications use-cases;
- More than 85 per cent of enterprises across multiple sectors are expecting up to 20 per cent ROI on various 5G/industry 4.0 use-cases;
Globally almost 51 per cent of the enterprises are looking to deploy 5G in conjunction with other wired and unlicensed wireless technologies; - The top technical and operational business challenges envisaged for deploying 5G in India are network integration with legacy networks, faster technological changes (or low adaptability in a multi-vendor ecosystem), proving ROI and timelines and inconsistent network infrastructure; and
- Targeting efficiency, quality management and new revenue models are prime areas where 5G is expected to be deployed by enterprises.
For a successful 5G roadmap and implementation, key aspects to be considered
For operators:
- There is a need to get the network engine rolling, hence CSPs will need to be swift in upgrading their cores to support all forms of communications. Network upgrades need continual focus on building network slicing, edge-AI compute models, beamforming, dynamic spectrum sharing, access technology-agnostic user equipment functioning and network analytics.
- It is imperative to build and market new 5G revenue streams. While robust networks and route to market are important in the 5G monetisation journey, it is equally important to protect margins by reducing total cost of ownership (TCO) by becoming a connected enterprise where front, back and mid office are connected through cloud native architecture where the traditional OSS, BSS are transformed and made nimbler
For government:
- A forward-looking policy paradigm that focusses on increasing the access of affordable services and devices across the nation is imperative;
- Rollout of 5G now needs to be backed by speedier fibre deployment to improve the tower fiberisation from current levels. Speedier inclusion of new sources from bus depots to railway stations to street poles and street furniture, agile deployment and faster maintenance of such assets will be crucial;
- R&D funding levels from the government need to improve in conjunction with policies that lay down financial incentives for participating members such as system integrators, CSPs and other infrastructure vendors; and
- The importance of personal data compliance is increased with 5G deployment. A viable option to improve defence against cyberattacks is to combine private network infrastructure with a zero-trust security strategy with an automated threat management system. However, a comprehensive policy can set the tone and direction of private 5G deployment in the country.















You must be logged in to post a comment Login